|

On this page we consider the theatre of ancient Greece, the history of theatre as it migrated from Greece to Rome, and
the history of Medieval theatre following the fall of the Roman Empire, a theatre dominated by an unlikely combination
of the Church and itinerant troupes of entertainers.
Greek Theatre
 If theatre is to be defined as involving the art of acting a part on stage, that is the dramatic impersonation of
another character than yourself, we begin with Thespis. A figure of whom we know very little, he won the play
competition in honor of the greek god Dionysus, in 534 B.C. While it is uncertain whether Thespis was a playwright, an
actor or a priest, it is his name with which the dramatic arts are associated in our word "Thespian". If theatre is to be defined as involving the art of acting a part on stage, that is the dramatic impersonation of
another character than yourself, we begin with Thespis. A figure of whom we know very little, he won the play
competition in honor of the greek god Dionysus, in 534 B.C. While it is uncertain whether Thespis was a playwright, an
actor or a priest, it is his name with which the dramatic arts are associated in our word "Thespian".
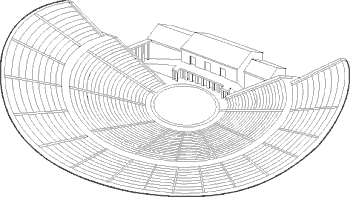
 Greek theatre took place in large (the largest ultimately
held twenty thousand people) hillside ampitheatres. The players included a chorus and their leader, and the "lines"
were more chanted than spoken. The chorus performed in the "orchestra", not on a raised stage. The use of masks to represent characters and high-soled boots worn to add height to the players limited
the movement of the actors. Indeed, the concept of "actors" themselves was not originally a part of Greek theatre,
but was developed as a consequence of certain playwrights of particular genius. Greek theatre took place in large (the largest ultimately
held twenty thousand people) hillside ampitheatres. The players included a chorus and their leader, and the "lines"
were more chanted than spoken. The chorus performed in the "orchestra", not on a raised stage. The use of masks to represent characters and high-soled boots worn to add height to the players limited
the movement of the actors. Indeed, the concept of "actors" themselves was not originally a part of Greek theatre,
but was developed as a consequence of certain playwrights of particular genius.
 Greek drama was dominated by the works and innovations of five playwrights over the 200 years following Thespis. The first three
of these were tragedians. Aeschylus (525-456 B.C.), who is most famous for his tragic trilogy the Oresteia,
introduced the concept of a second actor, expanding the possibilities for plot and histrionics through the interaction
of two characters in his dramas. While Aeschylus ultimately used a third actor, it was Sophocles (496-406 B.C.) who
actually initiated this innovation. Sophocles is most famous for his trilogy Oedipus Rex, and in his works the
role of the chorus in Greek drama diminishes in favor of the interplay between characters and the development of
character itself. It was Euripides (480-406 B.C.), however, while winning less competitions than Aeschylus or
Sophocles, who foreshadowed the ultimate form of drama as we know it -- employing a far more naturalistic or human
approach in his works, in contrast to the remote scale and formalized conventions used by his contemporaries. Greek drama was dominated by the works and innovations of five playwrights over the 200 years following Thespis. The first three
of these were tragedians. Aeschylus (525-456 B.C.), who is most famous for his tragic trilogy the Oresteia,
introduced the concept of a second actor, expanding the possibilities for plot and histrionics through the interaction
of two characters in his dramas. While Aeschylus ultimately used a third actor, it was Sophocles (496-406 B.C.) who
actually initiated this innovation. Sophocles is most famous for his trilogy Oedipus Rex, and in his works the
role of the chorus in Greek drama diminishes in favor of the interplay between characters and the development of
character itself. It was Euripides (480-406 B.C.), however, while winning less competitions than Aeschylus or
Sophocles, who foreshadowed the ultimate form of drama as we know it -- employing a far more naturalistic or human
approach in his works, in contrast to the remote scale and formalized conventions used by his contemporaries.
 The last two Greek playwrights were the authors of comedies: Aristophanes (448-380 B.C.) and Menander (342-292
B.C.). There was a separate competition for comedy which, while also dedicated to Dionysus, took place at the smaller
winter festival, rather than the major spring festival at which the tragedies were presented. As has been true
throughout the history of theatre, the comedies, dependent on topical humor and satire for much of their content, have
not survived the ages as well as tragedy -- which deals with more universal themes. However, the universal popularity
accorded these playwrights during their lifetimes attests to the significance which this dramatic form can have. The
popularity of their work, and the diminishing appeal of tragedy to the audiences of the time, can also be interpreted
as a comment on the role which theatre plays in society at large. Tragedy was at its height in Greek society when that
society was at its height, while comedy -- an outlet for the frustrations of society as well as a diversion for the
masses -- was most popular during the decline of Greek government. The last two Greek playwrights were the authors of comedies: Aristophanes (448-380 B.C.) and Menander (342-292
B.C.). There was a separate competition for comedy which, while also dedicated to Dionysus, took place at the smaller
winter festival, rather than the major spring festival at which the tragedies were presented. As has been true
throughout the history of theatre, the comedies, dependent on topical humor and satire for much of their content, have
not survived the ages as well as tragedy -- which deals with more universal themes. However, the universal popularity
accorded these playwrights during their lifetimes attests to the significance which this dramatic form can have. The
popularity of their work, and the diminishing appeal of tragedy to the audiences of the time, can also be interpreted
as a comment on the role which theatre plays in society at large. Tragedy was at its height in Greek society when that
society was at its height, while comedy -- an outlet for the frustrations of society as well as a diversion for the
masses -- was most popular during the decline of Greek government.
Roman Theatre
 The decline of Greek government and society coincided with the rise of the Roman Republic and subsequent empire. The Romans borrowed extensively
from Greek theatre. Although Roman theatre may not be held in the same high esteem as that of the Greeks, we have
inherited much from the influence of the Roman Theatre, including the word "play" itself, which derives from
a literal translation of the Latin word ludus, which means recreation or play. Roman theatre took two forms:
Fabula Palliata and Fabula Togata. Fabula Palliata were primarily translations of Greek plays into
Latin, although the term is also applied to the original works of Roman playwrights based upon Greek plays. We are
familiar with the latter from the works of Terence (190-159 B.C.), who introduced the concept of a subplot, enabling us
to contrast the reactions of different sets of characters to the same events or circumstances. The Fabula Togata
were of native origin, and were based on more broadly farcical situations and humor of a physical nature. An author of
some of the better examples of this type of drama is Plautus (c.250-184 B.C.). The decline of Greek government and society coincided with the rise of the Roman Republic and subsequent empire. The Romans borrowed extensively
from Greek theatre. Although Roman theatre may not be held in the same high esteem as that of the Greeks, we have
inherited much from the influence of the Roman Theatre, including the word "play" itself, which derives from
a literal translation of the Latin word ludus, which means recreation or play. Roman theatre took two forms:
Fabula Palliata and Fabula Togata. Fabula Palliata were primarily translations of Greek plays into
Latin, although the term is also applied to the original works of Roman playwrights based upon Greek plays. We are
familiar with the latter from the works of Terence (190-159 B.C.), who introduced the concept of a subplot, enabling us
to contrast the reactions of different sets of characters to the same events or circumstances. The Fabula Togata
were of native origin, and were based on more broadly farcical situations and humor of a physical nature. An author of
some of the better examples of this type of drama is Plautus (c.250-184 B.C.).
 Again, perhaps as a reflection of the society itself, performed drama in Rome consisted primarily of Fabula
Togata, as well as the spectacles of the gladiators and chariot races made familiar by modern Hollywood treatment
of the Roman Empire. Plays of a more serious literary nature continued to be written, but these were not intended
to be performed so much as read or recited. Although we have few works by Roman playwrights surviving to us in forms
that would lend themselves to revival, the influence of the Roman world on the form of the stage is one which had more
lasting effect. The semi-circular orchestra of the Greek theatre came to be eclipsed by the raised stage and the more
vigorous style style of acting employed by the performers. However, the greatest impact Rome may have had on the
theatre was to lower it in the esteem of the Church -- an impact that was to retard the growth of the dramatic arts for
several centuries. Again, perhaps as a reflection of the society itself, performed drama in Rome consisted primarily of Fabula
Togata, as well as the spectacles of the gladiators and chariot races made familiar by modern Hollywood treatment
of the Roman Empire. Plays of a more serious literary nature continued to be written, but these were not intended
to be performed so much as read or recited. Although we have few works by Roman playwrights surviving to us in forms
that would lend themselves to revival, the influence of the Roman world on the form of the stage is one which had more
lasting effect. The semi-circular orchestra of the Greek theatre came to be eclipsed by the raised stage and the more
vigorous style style of acting employed by the performers. However, the greatest impact Rome may have had on the
theatre was to lower it in the esteem of the Church -- an impact that was to retard the growth of the dramatic arts for
several centuries.
 The bent toward low comedy and its mass appeal -- coupled with its association with the entertainment of the arena
(which involved the martyrdom of early Christians) -- almost certainly contributed to its disfavor by officials of the
early Christian Church. Plays, or ludii were associated with either comedy of a coarse and scurrilous nature, or
with pagan rituals and holidays. It was the latter, however, which may account for the survival of theatre through the
Middle Ages. The bent toward low comedy and its mass appeal -- coupled with its association with the entertainment of the arena
(which involved the martyrdom of early Christians) -- almost certainly contributed to its disfavor by officials of the
early Christian Church. Plays, or ludii were associated with either comedy of a coarse and scurrilous nature, or
with pagan rituals and holidays. It was the latter, however, which may account for the survival of theatre through the
Middle Ages.
Medieval Theatre
 Some have written that theatre died following the
fall of the Roman Empire, and its memory was kept alive only in the performances of roving bands of jongleurs: itinerant
street players, jugglers, acrobats and animal trainers. However, while such troupes did help to maintain certain aspects of
theatrical art, particularly that involving stock characters, the Church itself contributed to the preservation of theatre. Some have written that theatre died following the
fall of the Roman Empire, and its memory was kept alive only in the performances of roving bands of jongleurs: itinerant
street players, jugglers, acrobats and animal trainers. However, while such troupes did help to maintain certain aspects of
theatrical art, particularly that involving stock characters, the Church itself contributed to the preservation of theatre.
 It is ironic that the Church, which caused theatres to be outlawed as the Roman Empire declined and then fell, was
one of the primary means of keeping theatre alive through the Middle Ages. This resulted from the Church's need to
establish itself in the community -- a community still steeped in pagan ritual and superstition which manifested itself
in seasonal festivals. The Church ultimately linked its own religious holidays with these seasonal festivals and began
to use dramatic form to illustrate the stories underlying these holidays so as to reinforce their religious connotation
and to better communicate the stories to an illiterate congregation. It is ironic that the Church, which caused theatres to be outlawed as the Roman Empire declined and then fell, was
one of the primary means of keeping theatre alive through the Middle Ages. This resulted from the Church's need to
establish itself in the community -- a community still steeped in pagan ritual and superstition which manifested itself
in seasonal festivals. The Church ultimately linked its own religious holidays with these seasonal festivals and began
to use dramatic form to illustrate the stories underlying these holidays so as to reinforce their religious connotation
and to better communicate the stories to an illiterate congregation.
 At first the parts played in these simple religious re-enactments of the nativity and adoration of the Magi were
played by priests in the sanctuary of the church. However, as the repertoire of the Church grew to include the passion
and crucifixion of Christ, the Church was confronted with the dilemma of how a priest should portray Herod. While
division of opinion in the Church continued as to the worth of dramatic interpretations, the members of the
congregation clearly enjoyed and were moved by them. The dramas continued to grow, moving out of the sanctuary and into
the open air in front of the Church. Ultimately, the members of town guilds began to contribute to these dramas, which
continued to grow more elaborate with time. Known as passion plays, miracle plays and morality plays, they continued
their close connection with the Church and church holidays, but began to introduce elements of stock characters that
were more contemporary in nature. With the growth of towns and the introduction of stable governments in Europe, the
stage was set for the Protestant Reformation, the Catholic Counter-Reformation and the secularization of theatre as it
emerged from the influence of the Medieval Church. At first the parts played in these simple religious re-enactments of the nativity and adoration of the Magi were
played by priests in the sanctuary of the church. However, as the repertoire of the Church grew to include the passion
and crucifixion of Christ, the Church was confronted with the dilemma of how a priest should portray Herod. While
division of opinion in the Church continued as to the worth of dramatic interpretations, the members of the
congregation clearly enjoyed and were moved by them. The dramas continued to grow, moving out of the sanctuary and into
the open air in front of the Church. Ultimately, the members of town guilds began to contribute to these dramas, which
continued to grow more elaborate with time. Known as passion plays, miracle plays and morality plays, they continued
their close connection with the Church and church holidays, but began to introduce elements of stock characters that
were more contemporary in nature. With the growth of towns and the introduction of stable governments in Europe, the
stage was set for the Protestant Reformation, the Catholic Counter-Reformation and the secularization of theatre as it
emerged from the influence of the Medieval Church.
|
|